Secondary Gamma Prime
Increased heat inputs, in terms of higher pouring temperature and mold temperature, result in reduced particle
size of secondary gamma prime. The level of vacuum and the number of shell coats affect the morphology of
the secondary gamma prime to a lesser extent . The morphology of the secondary gamma prime controls
the elevated temperature properties of Ni-base superalloys and, therefore, the knowledge of the effect of the
processing variables on the morphology the secondary gamma prime seems to be quite important.
Fluidity
While adequate literature is available pertaining the effect of various alloying elements on the structure and
mechanical properties of investment cast Ni-base superalloys, there is hardly any information on fluidity, which
is one of the most important casting characteristics of Ni-base superalloys cast in investment shells.
Woulds and Benson reported that Ni-base superalloys high pouring temperature (1550°C), as compared
to mold preheating temperature (1100°C), generates additional heat and instantaneous out-gas that becomes
trapped in the mold and creates “no-fill” areas.
Brezina and Kondic noticed that increased investment shell coatings reduced permeability of the mold wall,
promoted chemical reaction of molten metal with entrapped air and consequently increased the surface tension and
reduced fluidity. Vacuum was found to assist fluidity of the Ni-base superalloys either by reducing the back pressure
inside the mold and/or elimination the reaction of oxygen with reactive elements in the alloy composition and thus
reducing the surface tension of the molten alloy .
Fluidity of PK24 (IN-100) alloy has been found to be quite satisfactory. Individual processing variables do
affect the fluidity, but the combined effect of two or more variables on fluidity is much more pronounced.
Although all the foundry variables exert influence on fluidity, the maximum effect is imposed by pouring
temperature and mold temperature. Realizing satisfactory fluidity through judicious combinations of the
processing variables has been proved to be a distinct possibility .
NEW TRENDS
14.2. In investment casting
Rapid prototyping
Traditionally, investment casting has been the manufacturing process of choice for certain types of castings.
Ignoring for the moment those applications where investment casting is used to obtain specific material
properties, users choose investment casting as a manufacturing process primarily based on two variables.
The first variable is the complexity of the geometry. For purposes of this discussion, we can define geometric
complexity as features which increase the difficulty of manufacture such as undercuts, thin walls, increased
accuracy, etc., Investment casting is chosen when the geometry of the casting is more complex than can be
easily created by other casting methods such as sand casting, die casting or permanent mold casting. If a casting
would require multiple cores to be sand cast or multiple tool actions to be die cast, then investment casting is
considered.
The second variable is production volume. If the volume is too low, the amortized cost of wax pattern tooling
will likely make the casting more expensive than a machined part or weldments. Investment casting is only
considered when the volume is high enough that the cost of casting drops below the most of machined parts or
weldments .
Rapid prototyping technologies:
1- Stereo Lithography (SLA). 4- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
2- Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM). 5- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
3- Solid Ground Curing (SGC). 6- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
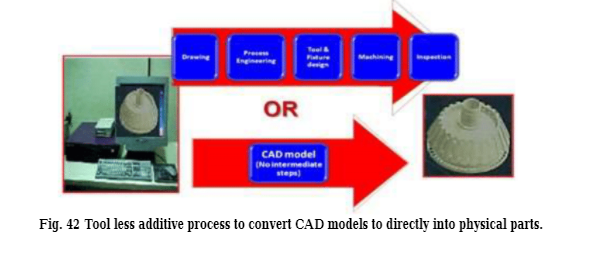
Figure 42 shows that the Rapid Prototyping (RP) technology saves time, especially for complex patterns shown in
Fig. 43, through using CAD models. Figures 44 and 45 show the silicon mold and wax prototype pattern for
investment casting made by RP .