It is widely believed that there is a need for a better correlation between casting and microstructure of Ni-superalloys.
Generally, the microstructure and properties of investment castings are influenced by the following parameters:
1. Superheat of liquid metal.
2. Pouring temperature
3. Shell mold temperature
4. Metal-mold-equilibrium (MME) temperature
5. Time taken to reach MME point
6. Cooling rate during solidification
The main findings of the effect of the casting processing variables on microstructural features may be
concluded in the following :
Grain Size
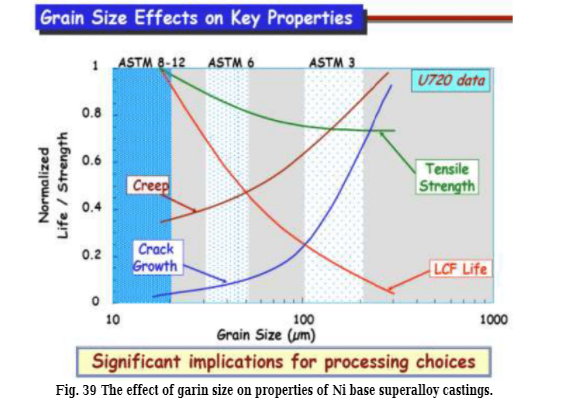
As all the casting properties are influenced by the grain size, selection of the optimum processing variables,
based on these considerations, seems to be essential.
For Ni-base superalloys IN-100, the grain size was shown to increase with pouring temperature and/or mold
temperature, with the effect of pouring temperature more pronounced. The coarser grains are promoted in
thicker sections as well as at increased vacuum level, whereas the effect of the number of coats is negligible
.
For investment cast IN713LC superalloy, low mold preheat temperature exhibits better controllability on grain
size over the variation of pouring temperature, whereas, contrary to grain size control, high mold preheat
temperature leads to better controllability of grain uniformity .
The effect of pouring temperature and superheat time on grain size is shown in Fig. 38.
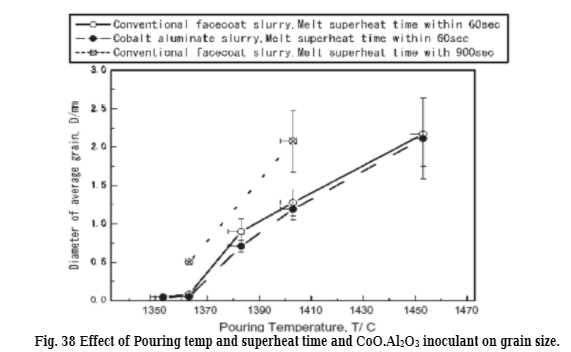
As the superheat time is increased the grain size increases as well as the increase in pouring temperature. The grain size was found to be slightly
affected by the variation of inoculant content (CoO.Al2O3) . Figures 39 and 40 illustrate the effect of Grain
size on the properties of Ni base superalloy castings.

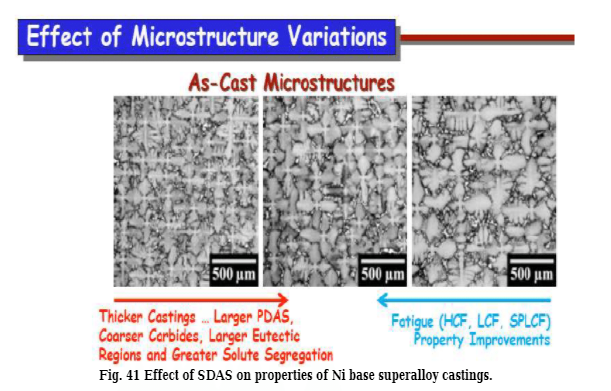
Microporosity and Dendrite Arm Spacing (DAS)Variations in DAS of IN-100 follow a trend similar to that of grain size, with the mold temperature playing a moreprominent role in determining the DAS than the pouring temperature and the level of vacuum. The influence of the number of shell coats on DAS is negligible .
Microporosity of investment cast turbine blade of IN-713LC superalloy decreases with decreasing secondary dendrite
arm spacing (SDAS). Inoculant was shown to exert some effect on decreasing the porosity content, particularly at high mold temperatures. Porosity exists at grain boundary and interdendritic regions. Since SDAS is much finer than
the grain size, the porosity content was considered to be rather a “weighing average” measure of SDAS than grain
size . Mold temperature exerts major effect on the porosity content because mold
temperature affects the cooling rate of casting and therefore its SDAS. When the mold temperature is high and
SDAS relatively large, refinement of grain size reduces the “effective” SDAS and therefore reducing the
porosity content. SDAS affect the properties of Ni base superalloy castings as shown in Fig. 41.